Capturing Bluetooth traffic with TCPDUMP
- #bluetooth
- #wireless
What’s Bluetooth?
Bluetooth, it’s a wireless industry standard registered in the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers under IEEE 802.15.1 It’s short-distance energy transmitted by low-powered radios, it’s used to exchange data and handle communication between Bluetooth devices. The Bluetooth concept was developed initially for portable devices like; cellphones, headsets, wireless speakers, and headphones, but nowadays is almost everywhere. Please refer to the following link to learn more about Bluetooth, and the advanced Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE).
Now, if you are curious and you want to learn how to capture Bluetooth traffic and analyze it with Wireshark, this is the best place to be…
Requirements
-
A Computer running Linux with an integrated interface dedicated to Bluetooth. (I’m currently running Ubuntu 18.04.0) you can use a Bluetooth adapter that supports a monitor or promiscuous mode for this task as well.
-
A second Bluetooth-capable device to connect to your Linux machine (it could be a device like; an iPhone, Android, or any other device of your preference) I will use a MacBook Pro running macOS Catalina 10.15.6.
-
The network protocol analyzer Wireshark, it’s a powerful tool, open-source, and you can download it here
I’m currently running Wireshark version 2.6.10
Preparing
Let’s check our Ubuntu machine:
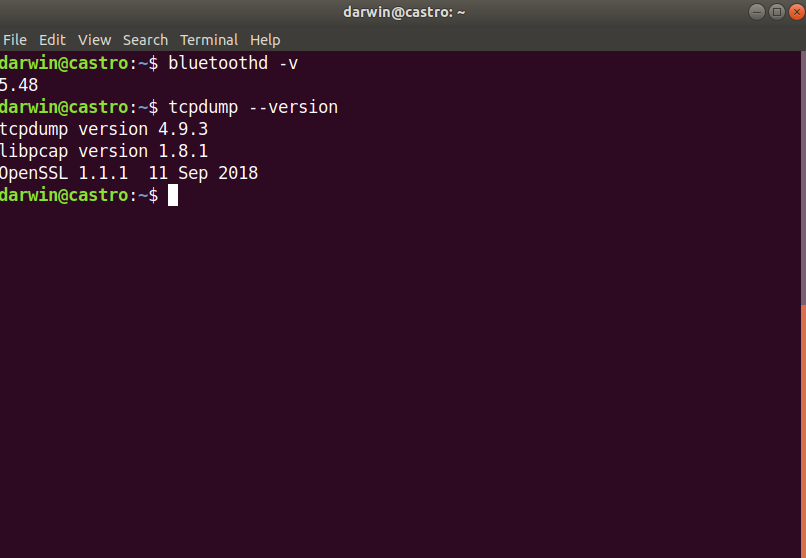
- In Ubuntu, open the terminal and run:
bluetoothd -vTo know if you have installed BlueZ in your distro, also run
tcpdump --versionKnow if you have TCPdump & Libpcap installed, those are required to accomplish this task.
The result will be something like this:
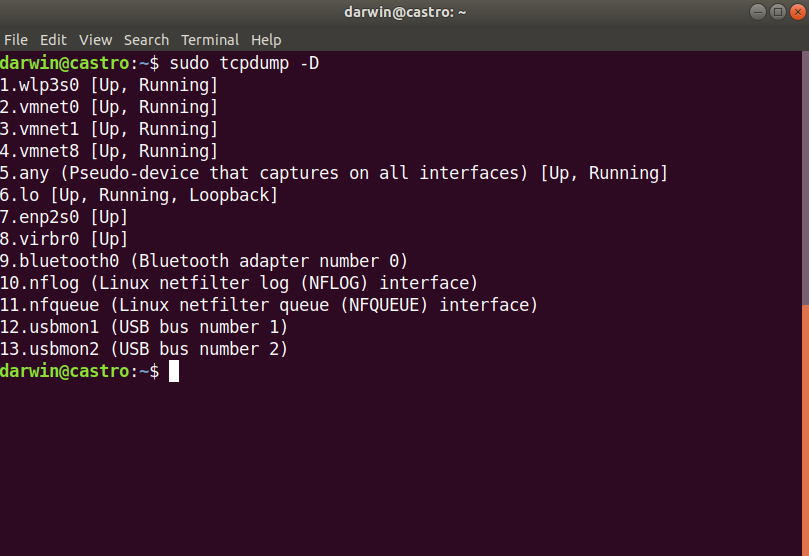
- With administrator privileges run:
sudo tcpdump -DTo confirm if your Bluetooth card is up and running, also copy the name of your Bluetooth card (in my case is bluetooth0).
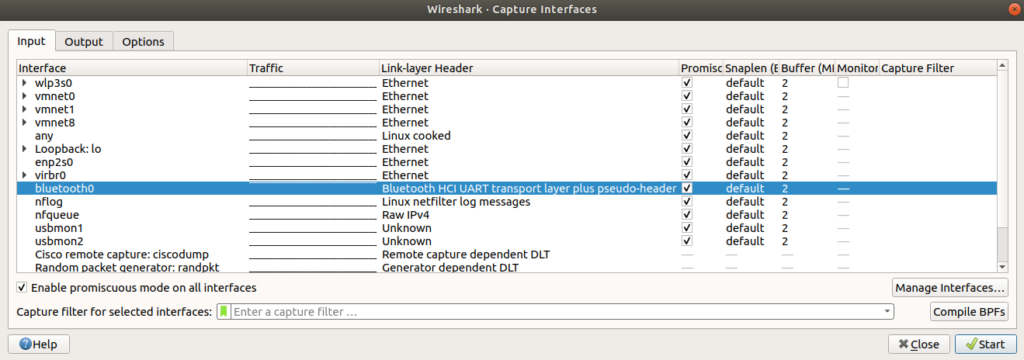
- Let’s check if the Bluetooth interface is turned ON in the second device, and make sure that you don’t have restrictions to share content using Bluetooth, for example, on my Mac machine I went to Sharing and I enabled the Bluetooth Sharing option there.
Capturing
- In your terminal run:
tcpdump -i bluetooth0 -w capturing_bluetooth.pcap(-i stands for interface > paste the name of your card previously copied, -w stands for write > use any name of your preference, at the end of the name put .pcap which is the file extension for Wireshark)
Your input should be like this:
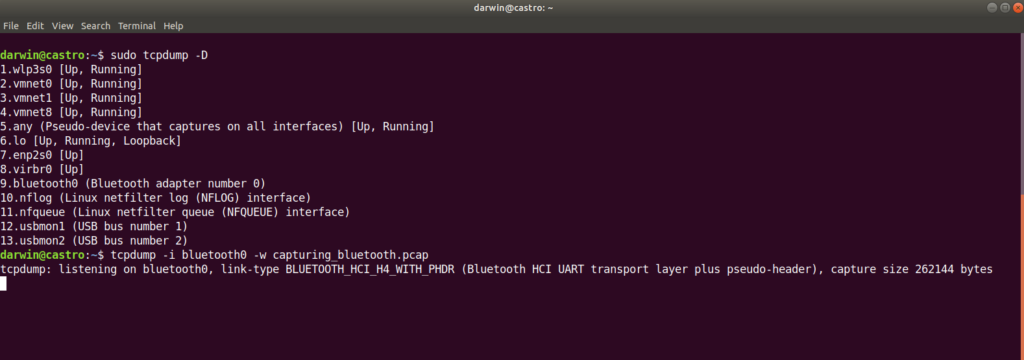
With the previous command, we set our Bluetooth interface in promiscuous mode, which means it will send and receive all the packets as normal, but also it will collect and save those packets for future analysis.
-
Let’s connect via Bluetooth Mac and the Ubuntu machine.
-
Let’s generate some Bluetooth traffic between both, in my scenario I just sent a .png image.
-
Finish the packet capture with the shortcut: Ctrl + c
-
In the Ubuntu machine Go to your Home directory, locate the .pcap file and open it (it should open using Wireshark by default if it doesn’t open Wireshark and go to File > Open and locate the file under /Home directory.
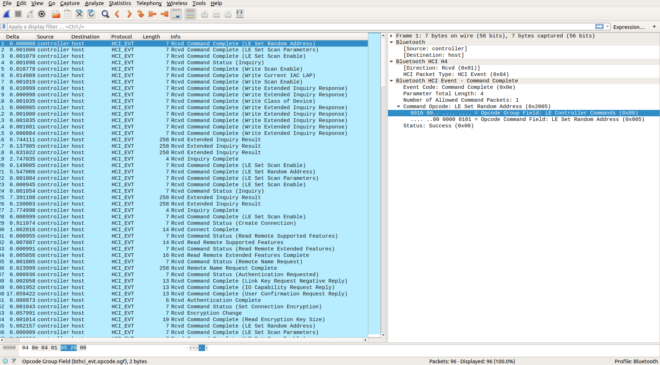
Voila!!! you captured Bluetooth traffic using your Ubuntu machine.
I hope you have enjoyed this quick reference to How to Capture Bluetooth Traffic in Ubuntu.
Please take care, keep social distancing, and don’t go outside without a face mask!