Wireless Authentication using EAP-TLS Protocol
- #wireless
- #security
Extensible Authentication Protocol-Transport Layer Security
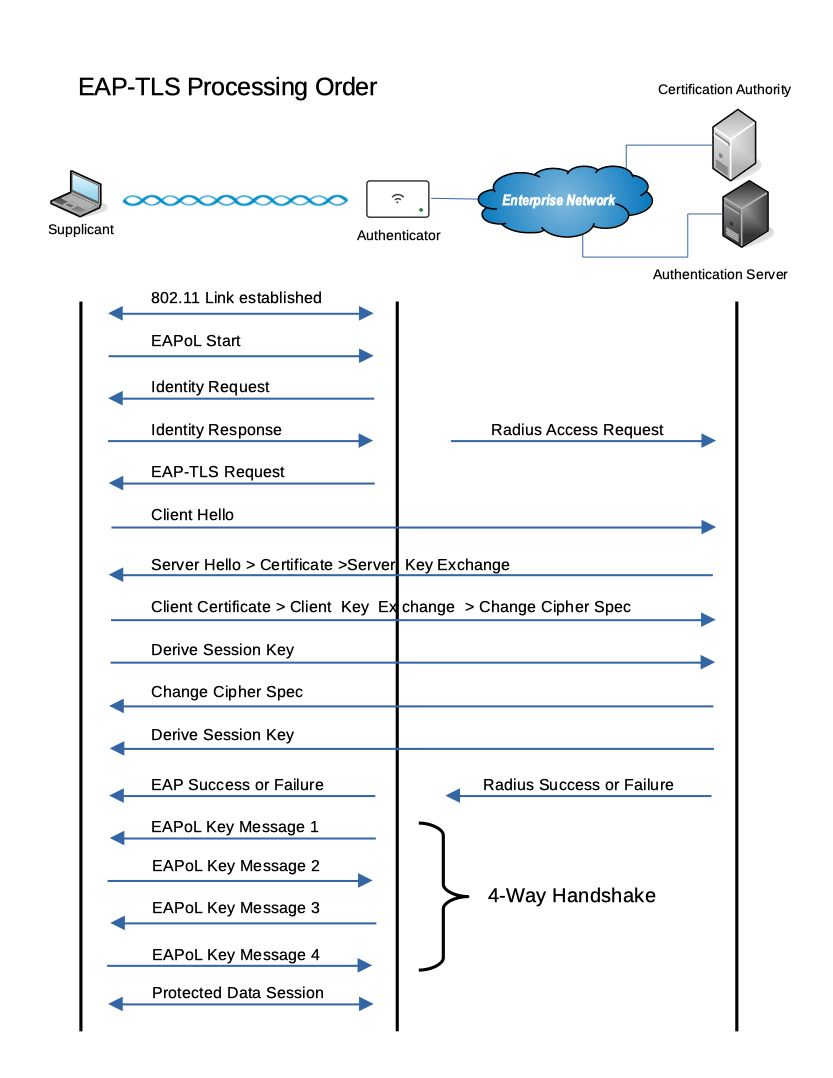
It’s well defined by the RFC 5216 as the most secure EAP standard available, EAP-TLS requires mutual certificate-based and key derivation in order to authenticate the supplicants, both “Supplicants and the Authentication server” will verify their identities and they must agree to succeed.
On the other hand, it’s a complete challenge to maintain a PKI infrastructure & manage client certs.
Let’s take a look at the following wireless packet capture that shows the entire process, the source MAC address: Alfa is the supplicant, and the MAC address ending: 37:b1 represents the Authenticator.
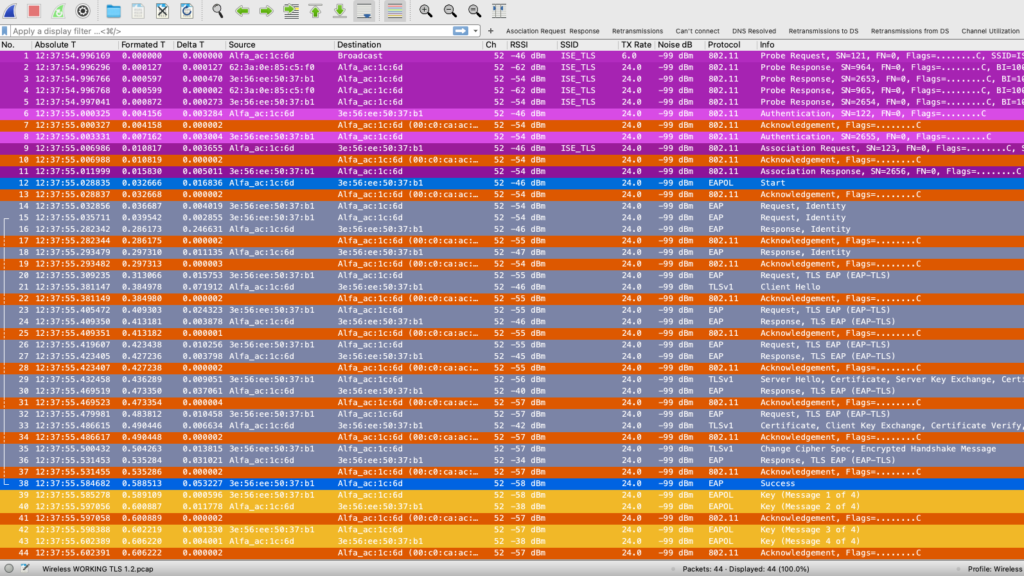
Now, let’s take a look into the interesting frames there:
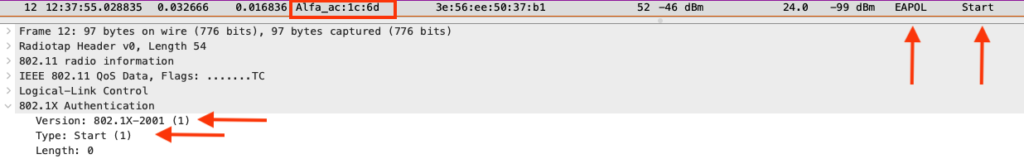
EAPOL Frame
Right after the 802.11 link negotiation, the supplicant sends an (optional) EAPOL frame to start the authentication.
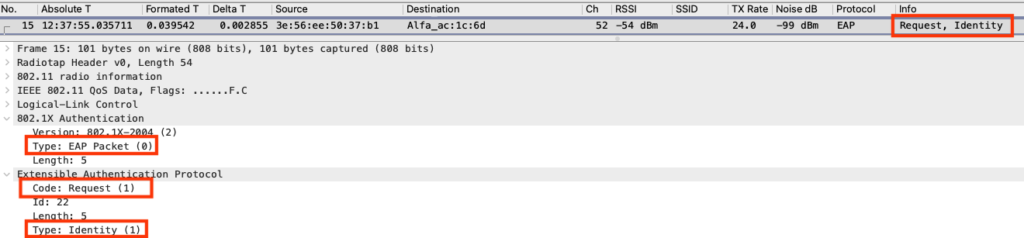
Identity Request
The authenticator responds by requesting the identity of the supplicant.
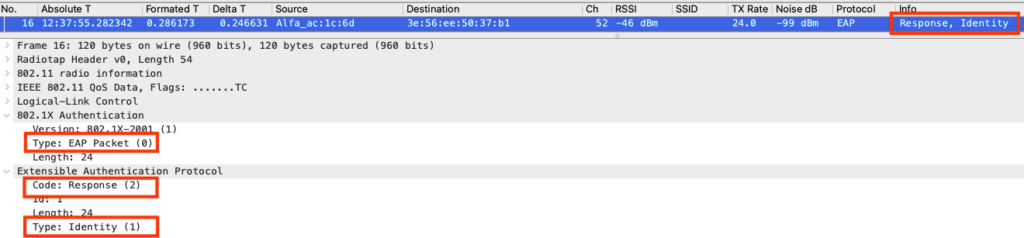
Identity Response
The supplicant responds with an “identity response frame”, and the Authenticator will forward the frame, and encapsulated it in a Radius request packet to the Authenticator Server.
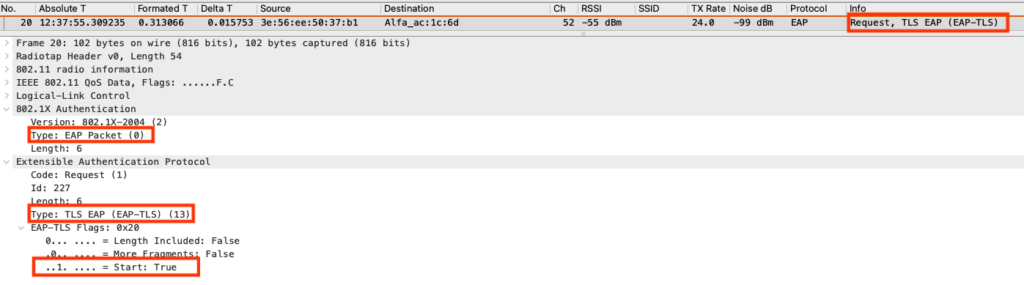
EAP-TLS Start
The Authenticator Server sends a Radius challenge to the supplicant, the Authenticator receives the challenge and translate it in an EAP-TLS start frame.
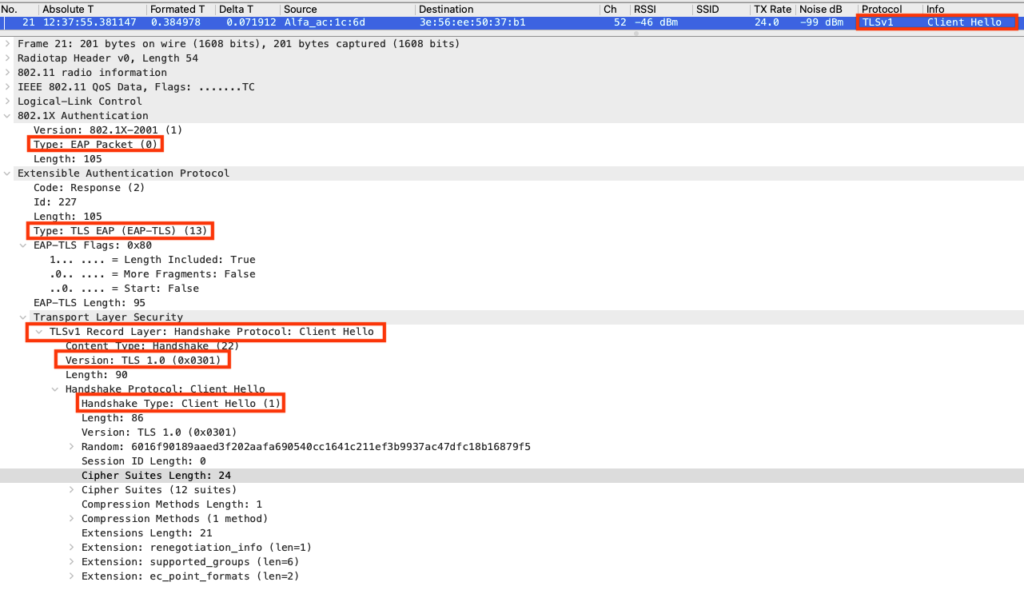
Client Hello
Supplicant sending a client hello to the server.
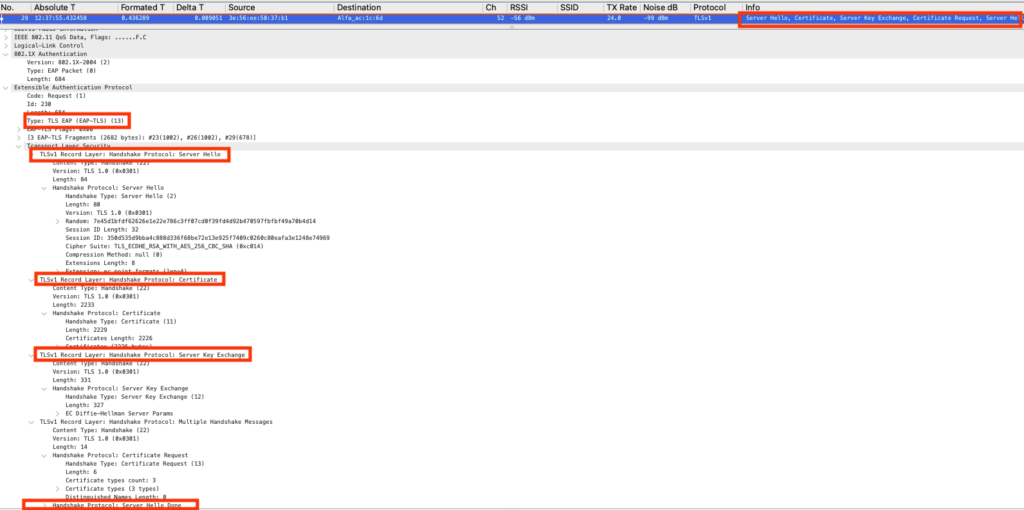
Server Hello
The Authenticator Server will send a server hello to the supplicant accompanied with a server certificate, a certificate request, and Server key exchange.
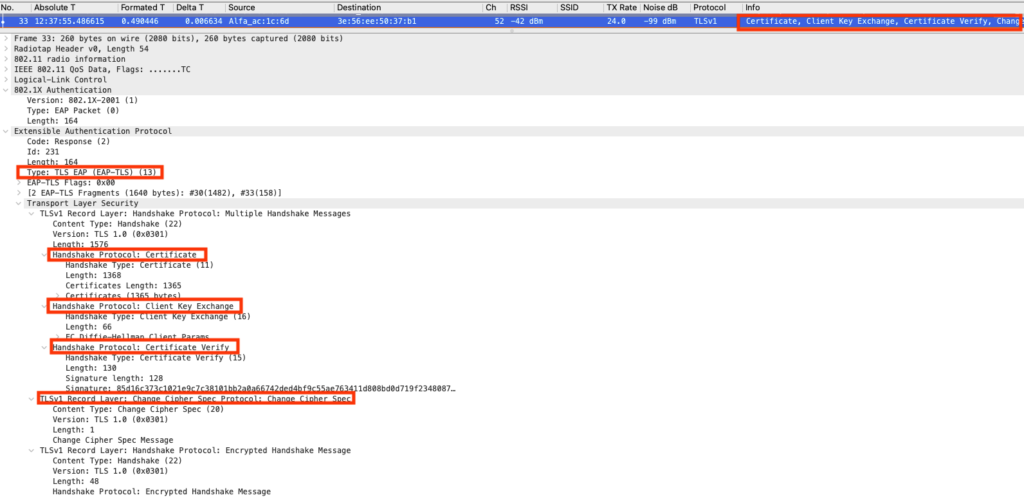
Client Certificate
The supplicant sends to the Authenticator server its certificate, the supplicant will verify the previous server certificate and it will change the cipher spec.
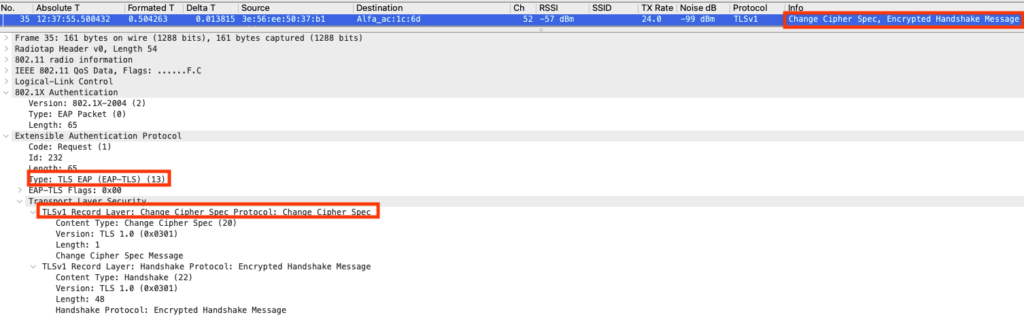
Sever Changing the Cipher Spec
The Authenticator server will reply to the supplicant changing the cipher spec as well.
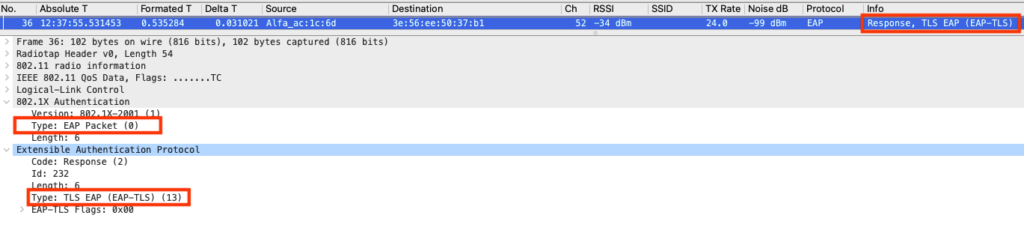
Supplicant EAP-Response
The supplicant responds and accepts the cipher change from the Authenticator Server.
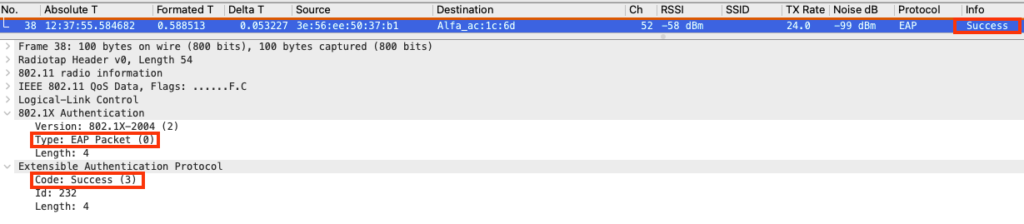
EAP-Success or failure
Depending on the case you will see the last frame regarding the EAP process as a success or failure.
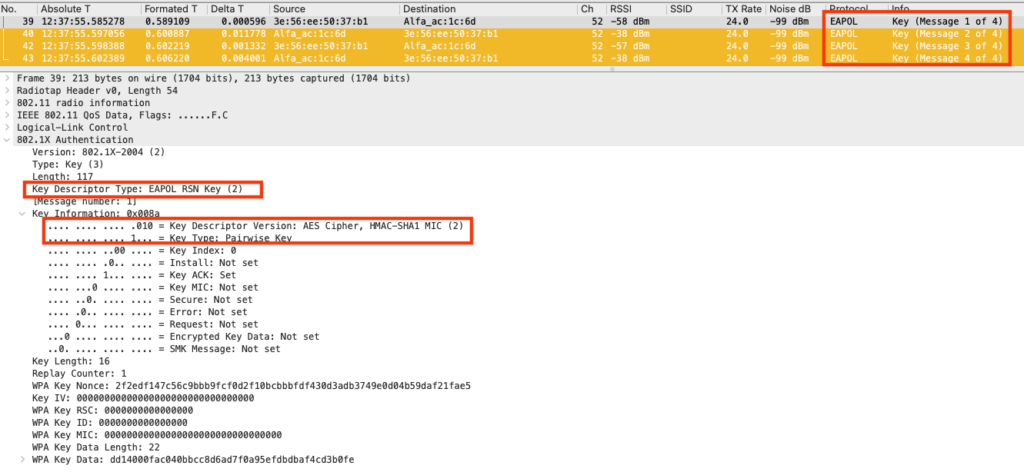
4-Way Handshake
After sending the EAP Success Frame, the Authenticator will start the 4-way handshake using EAPOL protocol, and it will attempt to establish an encrypted session with the supplicant.
If you want to run a test in your lab, the following link will provide some steps to play around with EAP-TLS.
As always, I hope that my short experience can answer any doubt during your CWDP journey, please stay safe, and protect yourself and others from Coronavirus (COVID-19)